Introduction
Domain names are a key part of the Internet infrastructure. They provide a human-readable address for any web server available on the Internet.
A domain name is an address of your website that people can type into our browser’s address bar to visit your website (Like you access the unityx.dev site to see this content).
In simple terms, your website as a house and your domain name will be its address.
Domain name Examples: facebook.com, google.com, unityx.dev..
I want a more detailed explanation :
The Internet is a large network of computers which each computer on this network can communicate with other computers.
To identify any computer is linked to a network, each computer is assigned an IP address (where IP stands for Internet Protocol). It’s an address made of a series of four numbers separated by dots, for example: 192.168.2.11.
That’s perfectly fine for computers, but IP addresses are hard to remember for people and might change over time.
To solve this problem we use human-readable addresses called domain names.
For example, I assume 173.194.121.32 (at the time of writing, this IP address can change) is the IP address of the domain name google.com. So to visit the google.com site, then you need to enter google.com into your browser’s address bar. The thing is the easier way, instead of you have to type 173.194.121.32.
Structure of domain names:
A domain domain name has a simple structure made of several parts (it might be one part only, two, three..), separated by dots and read from the right to left:
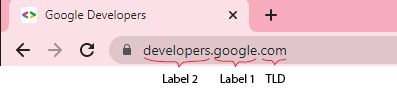
Domain google.com with a subdomain is developers:
Domain google.com without subdomain:
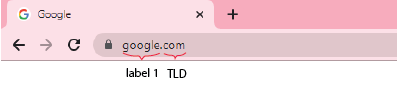
For beginners, only need the TLD and one label is enough to make a website (for example google.com, facebook.com, unityx.dev. Thus I recommend you to use it for simplicity.
Each of those parts provides specific information about the whole domain name.
TLD - Top Level Domain
TLDs or Top level domains tell users the general purpose of the service behind the domain name. The most popular is used are .com, .org, and .net that don’t require web services to meet any particular criteria, but some TLDs enforce stricter policies so it is clearer what their purpose is. For examples:
-
Country code top level domain - ccTLD : is a top level domain generally used or reserved for a country like .us for United States, .uk for United Kingdom. They are used by websites that want to target audiences in a specific country.
-
Sponsored top level domain - sTLD : is a specialized top level domain that has a sponsor representing by a specific community served by the domain. For example, .edu is only for use by educational and academic institutions, .gov are only allowed to be used by government departments.
Label or Component
The labels are what follow the TLD. A label is a case-insensitive character sequence anywhere from 1 to 63 characters in length, containing only the letters A through Z, digits 0 through 9, and the - character (which may not be the first or last character in the label). For example, game, 159, and my-house are all of valid labels.
The label located right before the TLD is also called s Secondary Level Domain (SLD).
A domain name can have many labels. It is not mandatory or necessary to have 3 labels to form a domain name. For instance, www.address.12.my-house.us is a valid domain name, but I recommended you shouldn’t use it. For clearly and easier to remember, you should use one label located right before the TLD like google.com, then you can create subdomains with different content located at each, such as developer.google.com, mail.google.com, or cloud.google.com.
How Domain Names Actually Work?
Note: At the most basic, you’ll need the following two things to start a website:
-
A domain name : this is an address of your website such as google.com
-
A web server : this is where your website is hosted.
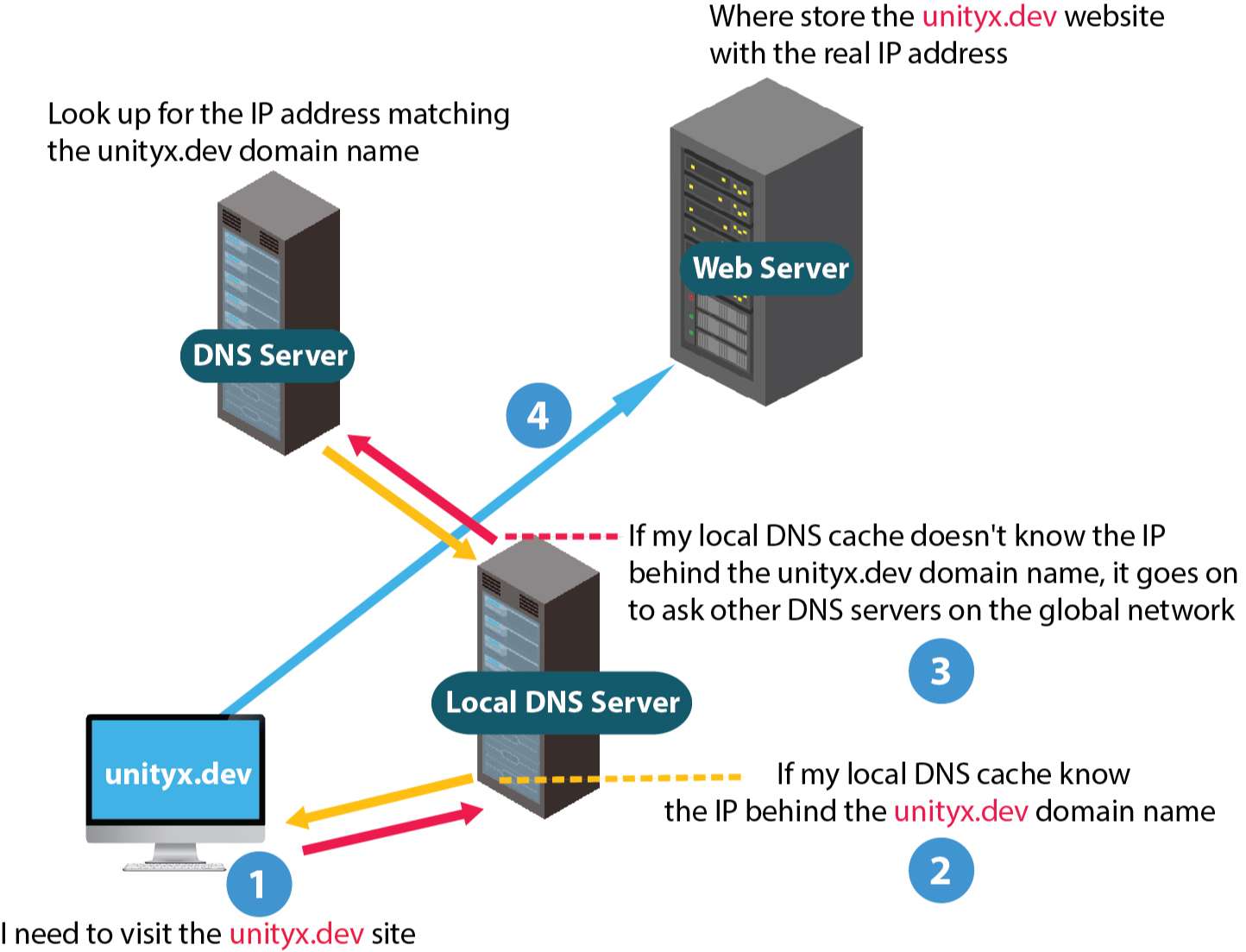
As we already know, when you want to visit a website, you need to type a domain name into your web browser. Let’s take a look at the processes:
-
Type unityx.dev in your browser.
-
Your browser asks your computer if it already recognizes the IP address matches with the unityx.dev domain name (using a local DNS cache). If it does, your browser already knows the real address of the unityx.dev site (where the unityx.dev site is live on), now your browser negotiates the contents with the web server to display it for you. End of story.
-
If your computer does not know which IP address matches the unityx.dev domain name, it goes on to ask other DNS servers on the global network. These servers then look up for the IP address matching the unityx.dev domain name.
-
Now that your computer knows the real address of the unityx.dev site, your browser can negotiate contents with the web server and display the content for you (Like the current contents you are reading).
How Domain Names Actually Work: